Overview
Tunneling over SSH provides a means where a local computer can open one or more connections over a secure encrypted channel to a remote computer system located somewhere else and from the remote computer a connection can be opened to another location. This process can be used to secure network traffic, bypass restrictions placed on a local network firewall, or establish a secure path into a private network that sits behind a firewall.
These instructions are specific to MacOS. In this knowledge base article, the remote server is a Linux system running Ubuntu Linux, however the same steps should work for a variety of *nix based systems.
An SSH tunnel must be specified at the localhost based on a particular protocol. In general, the best solution is to identify the application you want to tunnel, and use corresponding ports that exist above the priviledged ports range (https://www.w3.org/Daemon/User/Installation/PrivilegedPorts.html).
The example below is specific to the Chrome and Safari web browser. Additional settings and clients can be requested by submitting a new ticket or positing comments to this article.
WARNING
- SSH tunnelling is not a soluton that provides a fast connection. Network congestion and the process of encrypting and decrypting the connection (usually in software), will slow down the access speed.
- Some instructions, such as those specific to Safari, will remain in effect until disabled, i.e., the SSH tunnel will remain in effect until you undo the settings for the SSH tunnel.
Launch an SSH tunnel
To begin, you must initiate an SSH tunnel. Open the MacOS Terminal and connect to your remote server via SSH with the following flags:
ssh -D 8080 -N username@remotecomputer.eoas.ubc.ca
This will open port 8080 on your local system so any traffic to 8080 will be securely tunneled through to server remote computer at remotecomputer.eoas.ubc.ca.
Configure the Chrome web browser
The Chrome web browser from Google can leverage the local proxy as a socks5 proxy. To open a secure web browser, use the following command:
chrome --proxy-server="socks5://127.0.0.1:8080" --host-resolver-rules="MAP * 0.0.0.0 , EXCLUDE localhost"
The new Chrome browser will direct browsing traffice through the encrypted tunnel to the remote computer system where it will access the Internet.
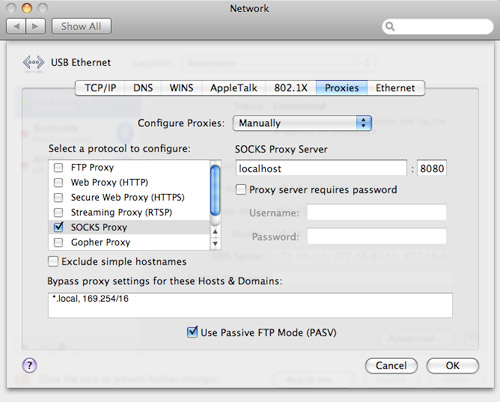
Configure the Safari web browser
Go to System Preferences » Network » Advanced » Proxies, and update your settings to reflect the settings in the screenshot below.